|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Variable Speed Drives |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Variable Speed Drives |
  
|
Available in v20
Available in All versions
Belt Speed Input Variables and Calculations
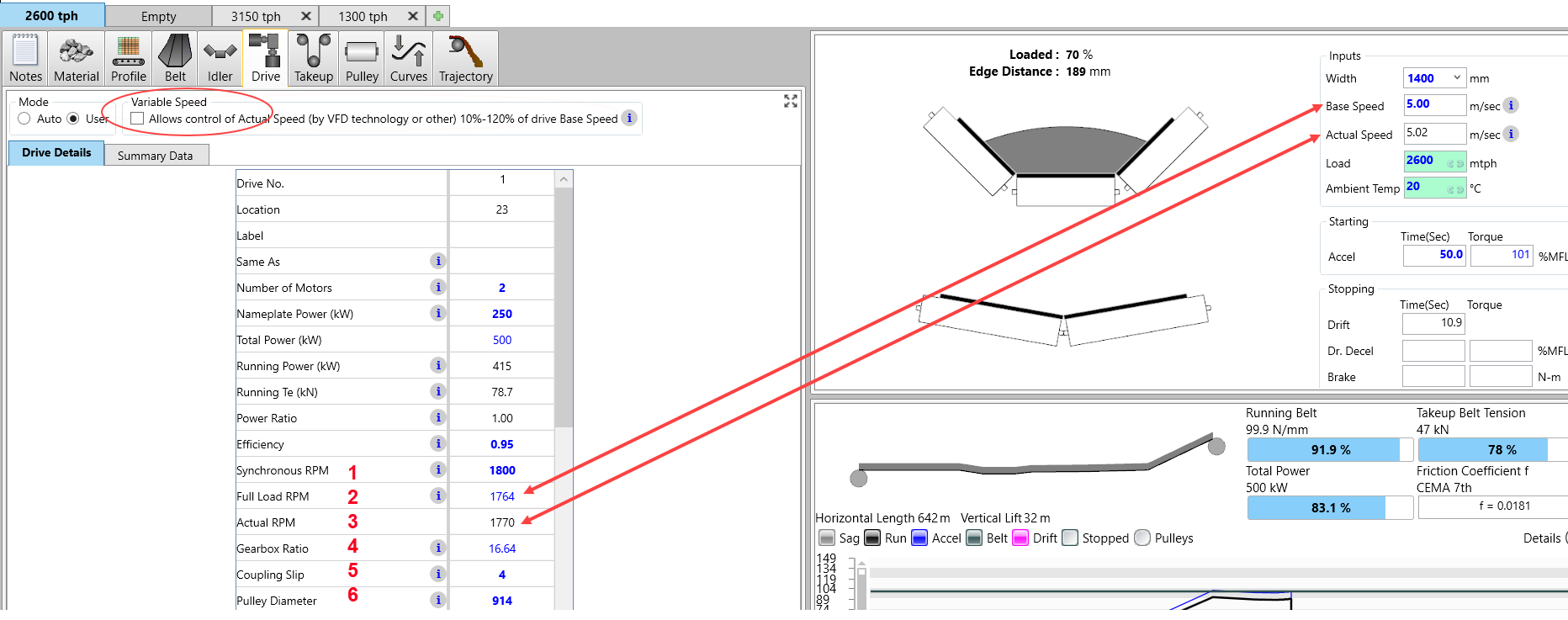
Belt Speed is now shown on the Main Screen as BASE SPEED and ACTUAL SPEED. BASE SPEED is calculated from "Full Load Motor RPM" (2), "Gearbox Ratio" (4), "Coupling Slip" i.e. Fluid Coupling (5) and "Pulley Diameter" (6) and represents the belt speed if the motor was running at "Full Load RPM".
If "Synchronous Motor RPM" (1),"Full Load Motor RPM" (2), "Coupling Slip" (5), "Pulley Diameter" (6) or BASE SPEED changes, the Gearbox Ratio (4) will automatically recalculate for each drive. If the "Gearbox Ratio" (4) of any drive is input by the user, the BASE SPEED is recalculated and changed and all other drive gearbox ratios are recalculated to match that BASE SPEED.
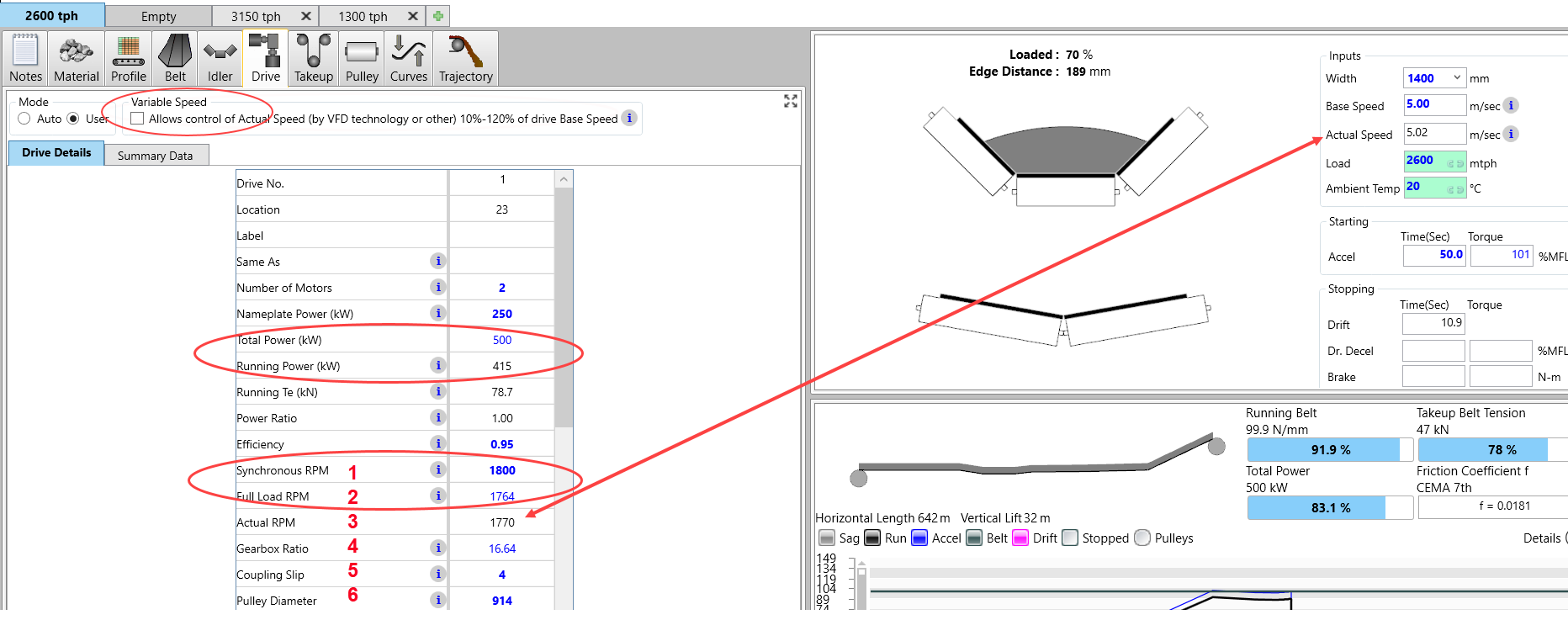
If the Variable Speed box is unchecked, the motor is operating in a fixed speed mode which means its speed will vary slightly based on its slip (the difference between "Synchronous RPM" (1) and Full Load RPM" (2)) and the ratio of "Running Power" to "Total Power" and is shown as "Actual RPM" (3) and ACTUAL SPEED on the Main Screen. If "Running Power" and "Total Power" are the same, the "Full Load RPM" and "Actual RPM" will be the same. The lower the "Running Power" to "Total Power" ratio, the faster the ACTUAL SPEED above BASE SPEED.
If the Variable Speed box is checked, the motor can operate in a variable speed mode which means the belt speed can vary between 10-120% of the "Full Load RPM (2) and BASE SPEED. ACTUAL SPEED on the Main Screen (and Actual Motor RPM) now becomes a User input and can vary between Cases.
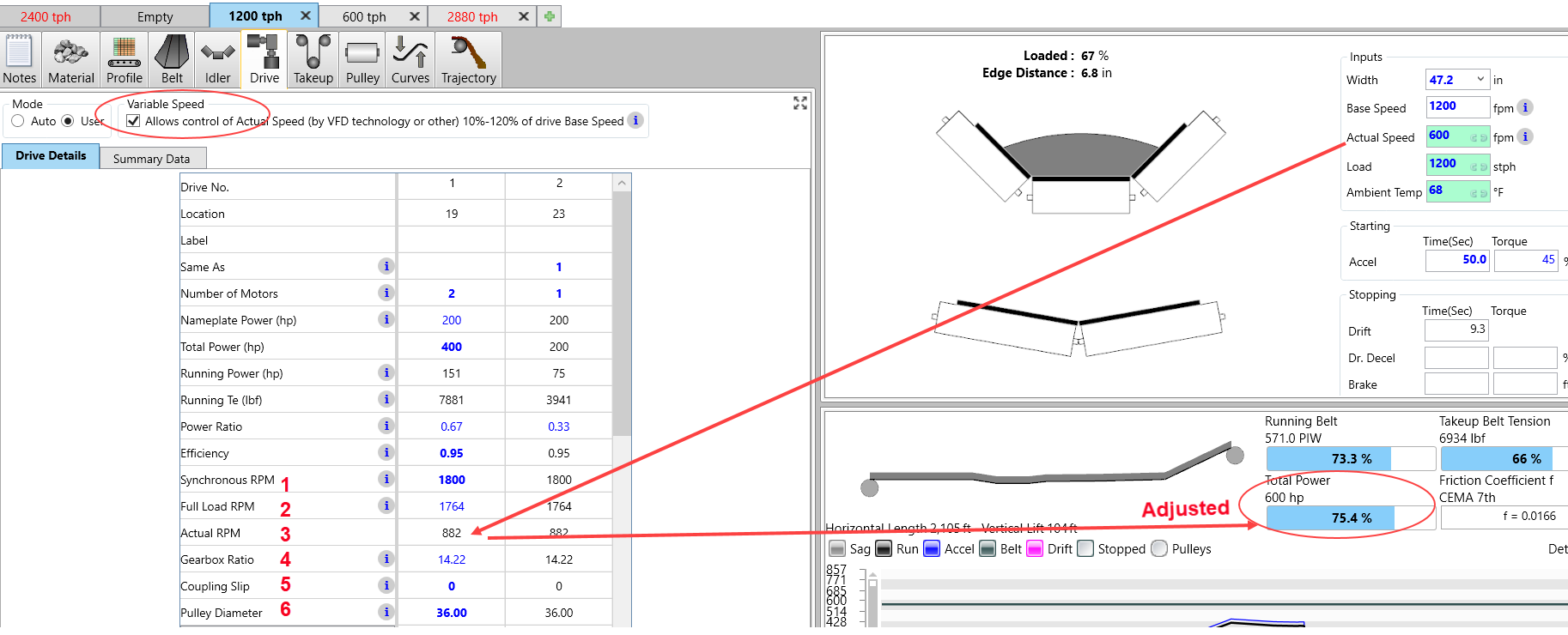
With a VFD, maximum torque output is constant up to synchronous speed and power is constant over synchronous speed. So if ACTUAL SPEED is less than BASE SPEED, the Percent Power Utilization is "Running Power"/"Total Power" divided by the ratio of ACTUAL SPEED/BASE SPEED. If ACTUAL SPEED is greater than BASE SPEED, the Percent Power Utilization is "Running Power"/"Total Power".