|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Idler Data |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Idler Data |
  
|
Auto DB or User DB mode is selected at the top.
![]()
•When the Auto DB mode is selected, the program selects the idler Description. The software will also search the idler database for other applicable idlers and allow the user to choose the Number of Rolls, Angle and Bearing Type if possible. Each selection may further restrict the list of available options.
The idler selection procedure searches for an idler that meets the required load rating and requested RPM and L-10 life criteria.
•In the User DB mode, the user can select the idler Description, Type, Belt Width, Number of Rolls, Angle, Bearing Type and Roll Material, if possible. The software will also search the idler database for other applicable idlers and after each selection may further restrict the list of available options.
•To Select the Custom mode, the user must be in the User mode first. Then change the Idler Selection from User to Custom.
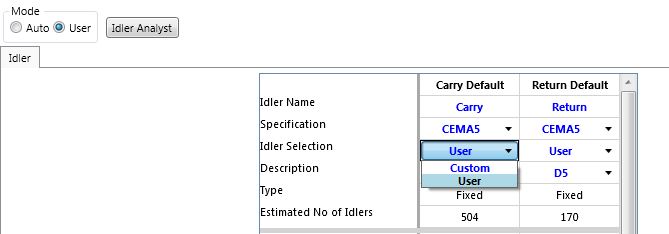
In the Custom mode, the user can/must input all the idler data without any reference to a database. Some of this data can only be changed by calling the Edit Data screen activated by clicking on the Edit Data button in the first row of the column.
When reading a conveyor file, if the file idler data does not agree with the database information, the file data will be used and the selection identified as Custom.
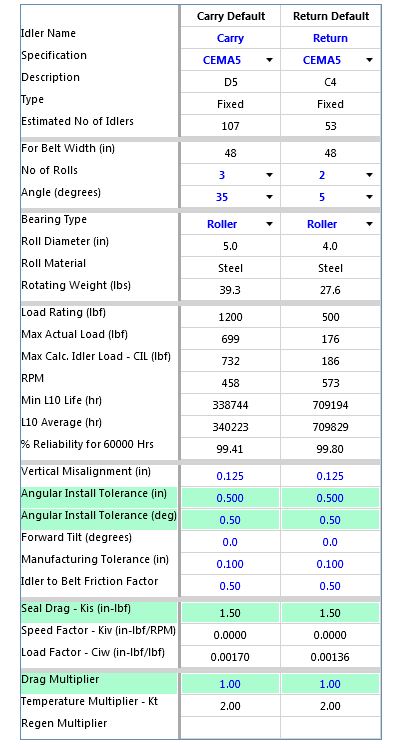
Everything in blue is editable. Everything that is red indicates an out-of-spec condition. Values that are bold are user input data; those that are normal type are auto select, default or calculated values.
•Specification is name of the database from which the idler is chosen. The pull-down box lists the databases available.
When using a database, the idler description and specification must be from one of the available databases; nevertheless, much of the data can be edited on this input screen. Idler descriptions can be added to the databases or edited by the Edit Idler Database procedures.
The carry and return idlers do not have to be selected from the same database, but they must both be either from a database or a custom input.
There are several available idler databases. "CEMA5" and "CEMA7" are associated with the two different handbook editions: the estimated drag values are taken from the respective edition. The idler database selection does not have to agree with the calculation method selected.
•The Description of the idler comes from the idler database and cannot be modified on this screen.
•The idler Type is either "Fixed" or "Garland". If it is specified in the database, it cannot be changed on this screen. If it is not specified in the database, it will be "Fixed" in Auto DB mode and user selectable in User DB or Custom mode.
•The Estimated No (number) of Idlers is shown. The value is an approximation based on the segment lengths and idler spacing input. This estimate does not include idlers in a feeder segment.
•The idler Width will be the same as the belt width in Auto DB mode. In the User DB mode, it can be selected from a list of available idlers from the database with widths greater than or equal to the belt width. In the Custom mode, this value is selected from the Edit Data screen.
•The No of Rolls and Angle can be selected from the pull down list of options contained in the selected database and limited by the application and other prior user selections. In Auto DB mode, the carry idler will be at least 3 rolls and 35º or greater; and, the return idler will be 1 or 2 rolls. In the User DB mode, the pull down list will have all the applicable idlers from the database. In the Custom mode, this value is selected from the Edit Data screen.
The selection of number of rolls and roll angle are interdependent in that the selection of one will limit the choices remaining for the other.
•The idler Bearing Type is either "Roller" or "Ball". If it is specified in the database, it cannot be changed on this screen. If it is not specified in the database, it will be selectable.
•The Roll Diameter of the idler comes from the idler database and cannot be modified on this screen.
•If Roll Material is specified in the database, it cannot be changed on this screen. If it is not specified in the database, it will be "Steel" in Auto DB mode and user selectable in User DB mode.
•Rotating Weight, Drag and Load Rating are all values that are accessed from the Edit Idler Database. In the User DB mode these values can be edited.
•The Max Actual Load, Max Calculated Idler Load, Roll RPM and L10 Life are calculated values.
The calculated idler load and minimum L10 life are used in the "Auto" mode to select the recommended idler.
If the actual idler RPM exceeds the value in the customized defaults or the Calculated Idler Load exceeds the Load Rating but the desired L10 life (in customized defaults) is not exceeded, a yellow condition is displayed indicating caution.
•Misalignment is the vertical height difference between idlers as described in the CEMA manual. This value is sometimes referred to as installation tolerance.
The input data used for calculating drag at the idler locations varies with the calculation method used. These are values that are accessed from the Edit Idler Database. In the User DB mode these values can be edited.
CEMA 5th: The method described in the "Belt Conveyors for Bulk Materials, 5th edition" handbook published by the Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association (CEMA). It is also called the CEMA Standard Historical Method in the 6th edition.
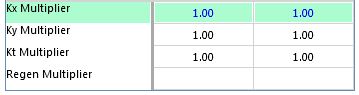
•The Kx and Ky Multipliers are factors are used to multiply the calculated drag. These values are input in the Customized Defaults form.
These drag multiplier are typically utilized to test the impact high or low drag values may have on the calculated power requirements, belt tensions, etc. ...
•The Kt Multiplier is the factor by which the calculated drag is multiplied to correct for the low temperature value entered on the main screen.
The value is base on the operating temperature input on the main screen and may not be edited here.
•The calculated drag is multiplied by the Regen Multiplier when the conveyor is regenerative. This value is input in the Defaults > Idler form.
The Regen multiplier is used to introduce some conservatism into the calculations since the highest regenerative power requirement typically goes with low drag.
CEMA 7th: The method described in the "Belt Conveyors for Bulk Materials, 7th edition" handbook published by the Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association (CEMA). It is called the CEMA Universal Method in the 7th edition.
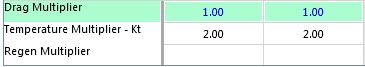
•The Drag Multipliers are factors are used to multiply the calculated idler drag. This value is input in the Customized Defaults form.
The drag multiplier is typically utilized to test the impact high or low drag values may have on the calculated power requirements, belt tensions, etc. ...
•The Temperature Multiplier is the factor by which the calculated drag is multiplied to correct for the low temperature value entered on the main screen.
•The calculated drag is multiplied by the Regen Multiplier when the conveyor is regenerative. This value is input in the Customized Defaults form.
The Regen Multiplier is used to introduce some conservatism into the calculations since the highest regenerative power requirement typically goes with low drag.
If the user wants to specify an idler that is not in the database, either a different database can be selected (Specification pull down list of available databases), the idler can be added to an idler database
The input and output for the pipe belt design is similar except that the number of rolls is fixed at 6 and the idler angle at 60 degrees.
See also: Edit Idler Database, Idler Specifications.