|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Electric Winch |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Electric Winch |
  
|
Available in v20
Available in All
A take-up method where the take-up pulley is mounted on a horizontal trolley attached to a wire rope guided by a series of sheaves to an electrically (or hydraulically) powered winch. The tension in the belt is generated by an electric motor. The electric motor can be controlled to continuously provide a specific torque (Always On mode) or can be controlled to allow an acceptable range of belt tension (On/Off mode). The term "On/Off" means the motor only turns on when the belt tension exceeds a high/low tension dead band (sometimes referred to as a 2-position winch). When the motor is turned off (inactive), the brake is set and the take-up is "Fixed". Anytime the winch is off (inactive), all belt tension in the system will fluctuate as the take-up tensions range between the high and low dead band settings.
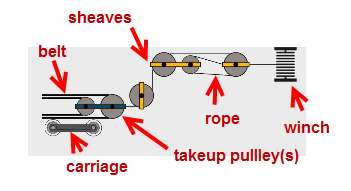
Pros
This option requires the smallest footprint and requires little vertical space. Can take advantage of mechanical sheaves to increase tension or increase travel therefore can be used on any conveyor length. When operated in “Always On” mode, the winch provides a consistent tension (similar to gravity) making it easier to predict belt tension requirements. When operated in “On/Off” mode, if the dead band is set properly, the winch should not run very often but only adjust for permanent belt stretch and ambient temperature fluctuations which should result in low maintenance.
Cons
A fail-safe brake must be employed and is generally set. When in On/Off mode, this control method is generally the slowest option and is not always able to keep up with transient conditions in the belt during stopping/starting. Therefore it is common to increase the dead band range during starting/stopping or keep the winch off (inactive) during starting/stopping. This generally increases system dynamics (increases all forces high and low) therefore advanced system design tools including flexible body transient analysis (dynamic analysis) is highly recommended when this option is chosen.